What is epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent unprovoked seizures.
What is the prevalence and how common is this disorder?
About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, with almost 90% of these people being in developing countries. Epilepsy is more likely to occur in young children, or people over the age of 65 years; however, it can occur at any time.
What are the causes of that disorder?
There are different causes of epilepsy that are common in certain age groups.
- During the neonatal period and early infancy the most common causes include hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, CNS infections, trauma, congenital CNS abnormalities, and metabolic disorders.
- During late infancy and early childhood, febrile seizures are fairly common. These may be caused by many different things, some thought to be things such as CNS infections and trauma.
- During childhood, well-defined epilepsy syndromes are generally seen.
- During adolescence and adulthood, the causes are more likely to be secondary to any CNS lesion. Further, idiopathic epilepsy is less common. Other causes associated with these age groups are stress, trauma, CNS infections, brain tumors, illicit drug use and alcohol withdrawal.
- In older adults, cerebrovascular disease is a very common cause. Other causes are CNS tumors, head trauma, and other degenerative diseases which are common in the older age group, such as dementia.
Is it possible for epilepsy to affect children schoolastic performance?
There is a well known epileptic syndrome called “ABSCENCE FITS”. It is seen more common in the childhood period , usually characterized by attacks of abscence and loss of concentration and attention without complete loss of conciouscness , usually the main complaining person is the teacher , that they noticed these attacks of staring and inattention.
Is there any investigations for this disorder?
We have 2 types of investigations:
The first one is radiological investigations , CT brain or MRI brain to study brain structure to exclude organic causes like haemorrahge , tumors , etc…….
The second one is neurophysiological studies as EEG.
As shown in next figure.
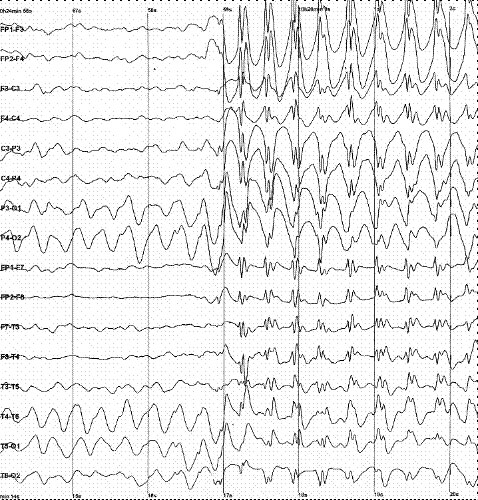
Generalized 3 Hz spike and wave discharges in EEG
Management
- Epilepsy is usually treated with medication prescribed by a, neurologists.
- Epilepsy is usually controlled, although surgery may be considered in difficult cases. However, over 30% of people with epilepsy do not have seizure control even with the best available medications.
- Not all epilepsy syndromes are lifelong – some forms are confined to particular stages of childhood. Epilepsy should not be understood as a single disorder, but rather as syndromic with vastly divergent symptoms but all involving episodic abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
DR. MOHAMED HAMDY IBRAHIM
MB.BChH, M.Sc (neurology), M.D. (neurology),
Lecturer at GMU and neurology specialist at GMC hospital, Ajman, UAE.





































